Data structures(indexed Sequential Search)
Indexed Sequential
Search
In this searching method, first of all,
an index file is created, that contains some specific group or division of
required record when the index is obtained, then the partial indexing takes
less time cause it is located in a specified group.
Characteristics of Indexed Sequential Search:
·
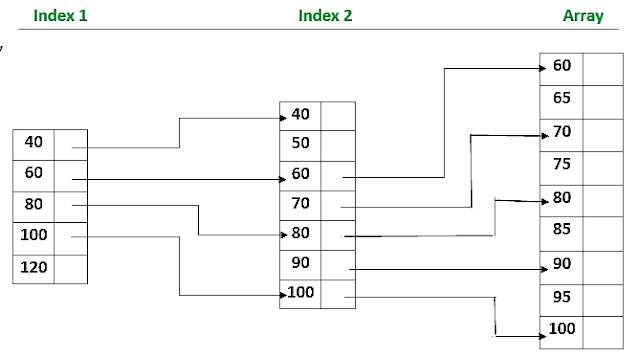
In Indexed Sequential Search a sorted index is set aside
in addition to the array.
·
Each element in the index points to a block of elements in
the array or another expanded index.
·
The index is searched 1st then the array and guides the
search in the array.
Note: Indexed Sequential Search actually does the indexing
multiple time, like creating the index of an index.
Explanation by diagram “Indexed
Sequential Search”:
void indexedSequentialSearch(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
int GN = 3; // GN is group number that is number of
//
elements in a group
int elements[GN], indices[GN], i, set = 0;
int j = 0, ind = 0, start, end;
for (i = 0; i < n; i += 3) {
//
Storing element
elements[ind]
= arr[i];
//
Storing the index
indices[ind]
= i;
ind++;
}
if (k < elements[0]) {
printf("Not
found");
exit(0);
}
else {
for (i = 1; i <= ind; i++)
if (k <= elements[i]) {
start
= indices[i - 1];
end
= indices[i];
set
= 1;
break;
}
}
if (set == 0) {
start
= indices[GN - 1];
end
= GN;
}
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (k == arr[i]) {
j
= 1;
break;
}
}
if (j == 1)
printf("Found
at index %d", i);
else
printf("Not
found");
}
// Driver
code
void main()
{
int arr[] = { 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//
Element to search
int k = 8;
indexedSequentialSearch(arr,
n, k);
}
Comments
Post a Comment