Data Structures( Traversals of a graph : BFS and DFS)
Graph Travesals:
Graph traversal is technique used for searching a vertex in
a graph. The graph traversal is also used to decide the order of vertices to be
visit in the search process. A graph traversal finds the egdes to be used in
the search process without creating loops that means using graph traversal we
visit all verticces of graph without getting into looping path.
There are two graph traversal techniques and they are as
follows...
DFS (Depth First Search)
BFS (Breadth First Search)
DFS (Depth First Search):
DFS traversal of a graph, produces a spanning tree as final
result. Spanning Tree is a graph without any loops. We use Stack data structure
with maximum size of total number of vertices in the graph to implement DFS
traversal of a graph.
We use the following steps to implement DFS traversal...
Step 1: Define a Stack of size total number of vertices in
the graph.
Step 2: Select any vertex as starting point for traversal.
Visit that vertex and push it on to the Stack.
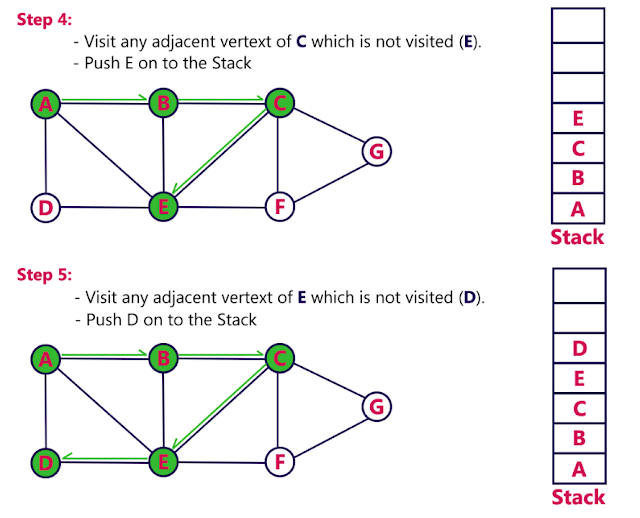
Step 3: Visit any one of the adjacent vertex of the verex
which is at top of the stack which is not visited and push it on to the stack.
Step 4: Repeat step 3 until there are no new vertex to be
visit from the vertex on top of the stack.
Step 5: When there is no new vertex to be visit then use back
tracking and pop one vertex from the stack.
Step 6: Repeat steps 3, 4 and 5 until stack becomes Empty.
Step 7: When stack becomes Empty, then produce final
spanning tree by removing unused edges from the graph
Back tracking is coming back to the vertex from which we came to current vertex.
Example

BFS (Breadth First Search):
BFS traversal of a graph, produces a spanning tree as final
result. Spanning Tree is a graph without any loops. We use Queue data structure
with maximum size of total number of vertices in the graph to implement BFS
traversal of a graph.
We use the following steps to implement BFS traversal...
Step 1: Define a Queue of size total number of vertices in
the graph.
Step 2: Select any vertex as starting point for traversal.
Visit that vertex and insert it into the Queue.
Step 3: Visit all the adjacent vertices of the verex which
is at front of the Queue which is not visited and insert them into the Queue.
Step 4: When there is no new vertex to be visit from the
vertex at front of the Queue then delete that vertex from the Queue.
Step 5: Repeat step 3 and 4 until queue becomes empty.
Step 6: When queue becomes Empty, then produce final
spanning tree by removing unused edges from the graph












Comments
Post a Comment