Data Structures(Binary search in Data structures)
Binary Search
👉 Binary search is the search technique which works efficiently on the sorted lists.
👉 Hence, in order to search an element into some list by using binary search
technique, we must ensure that the list is sorted.
👉 Binary search follows divide and conquer approach in which, the list is divided into two halves and the item is compared with the middle element of the list.
👉 If the match is found then, the location of middle element is returned otherwise, we search into either of the halves depending upon the result produced through the match.
👉 Binary search is implemented using following steps...
- Step 1 - Read the search element from the user.
- Step 2 - Find the middle element in the sorted list.
- Step 3 - Compare the search element with the middle element in the sorted list.
- Step 4 - If both are matched, then display "Given element is found!!!" and terminate the function.
- Step 5 - If both are not matched, then check whether the search element is smaller or larger than the middle element.
- Step 6 - If the search element is smaller than middle element, repeat steps 2, 3, 4 and 5 for the left sublist of the middle element.
- Step 7 - If the search element is larger than middle element, repeat steps 2, 3, 4 and 5 for the right sublist of the middle element.
- Step 8 - Repeat the same process until we find the search element in the list or until sublist contains only one element.
- Step 9 - If that element also doesn't match with the search element, then display "Element is not found in the list!!!" and terminate the function.
BINARY_SEARCH(A, lower_bound, upper_bound, VAL)
- Step 1: [INITIALIZE]
SET BEG = lower_bound
END = upper_bound, POS = - 1 - Step 2: Repeat Steps 3
and 4 while BEG <=END
- Step 3: SET MID = (BEG
+ END)/2
- Step 4: IF A[MID] =
VAL
SET POS = MID
PRINT POS
Go to Step 6
ELSE IF A[MID] > VAL
SET END = MID - 1
ELSE
SET BEG = MID + 1
[END OF IF]
[END OF LOOP] - Step 5: IF POS = -1
PRINT "VALUE IS NOT PRESENT IN THE ARRAY"
[END OF IF] - Step 6: EXIT
Complexity
|
SN |
Performance |
Complexity |
|
1 |
Worst case |
O(log n) |
|
2 |
Best case |
O(1) |
|
3 |
Average Case |
O(log n) |
|
4 |
Worst case space complexity |
O(1) |
Example
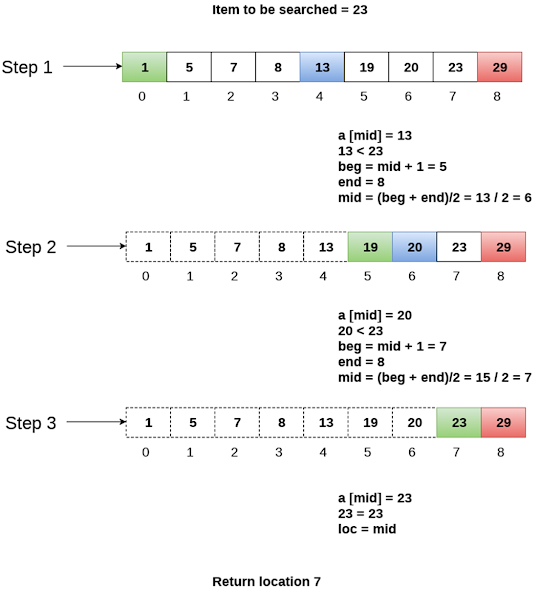
Let us
consider an array arr = {1, 5, 7, 8, 13, 19, 20, 23, 29}. Find the location of
the item 23 in the array.
In
1st step
:
1.
BEG = 0
2.
END = 8ron
3.
MID = 4
4.
a[mid] = a[4] = 13 < 23, therefore
in
Second step:
1.
Beg = mid +1 = 5
2.
End = 8
3.
mid = 13/2 = 6
4.
a[mid] = a[6] = 20 < 23, therefore;
in
third step:
1.
beg = mid + 1 = 7
2.
End = 8
3.
mid = 15/2 = 7
4.
a[mid] = a[7]
5.
a[7] = 23 = item;
6.
therefore, set location = mid;
7.
The location of the item will be 7.
Implementation of Binary Search Algorithm :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int first, last, middle, size, i, sElement, list[100];
clrscr();
printf("Enter the size of the list: ");
scanf("%d",&size);
printf("Enter %d integer values in Assending order\n", size);
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d",&list[i]);
printf("Enter value to be search: ");
scanf("%d", &sElement);
first = 0;
last = size - 1;
middle = (first+last)/2;
while (first <= last) {
if (list[middle] < sElement)
first = middle + 1;
else if (list[middle] == sElement) {
printf("Element found at index %d.\n",middle);
break;
}
else
last = middle - 1;
middle = (first + last)/2;
}
if (first > last)
printf("Element Not found in the list.");
getch();
}
Output

Comments
Post a Comment